
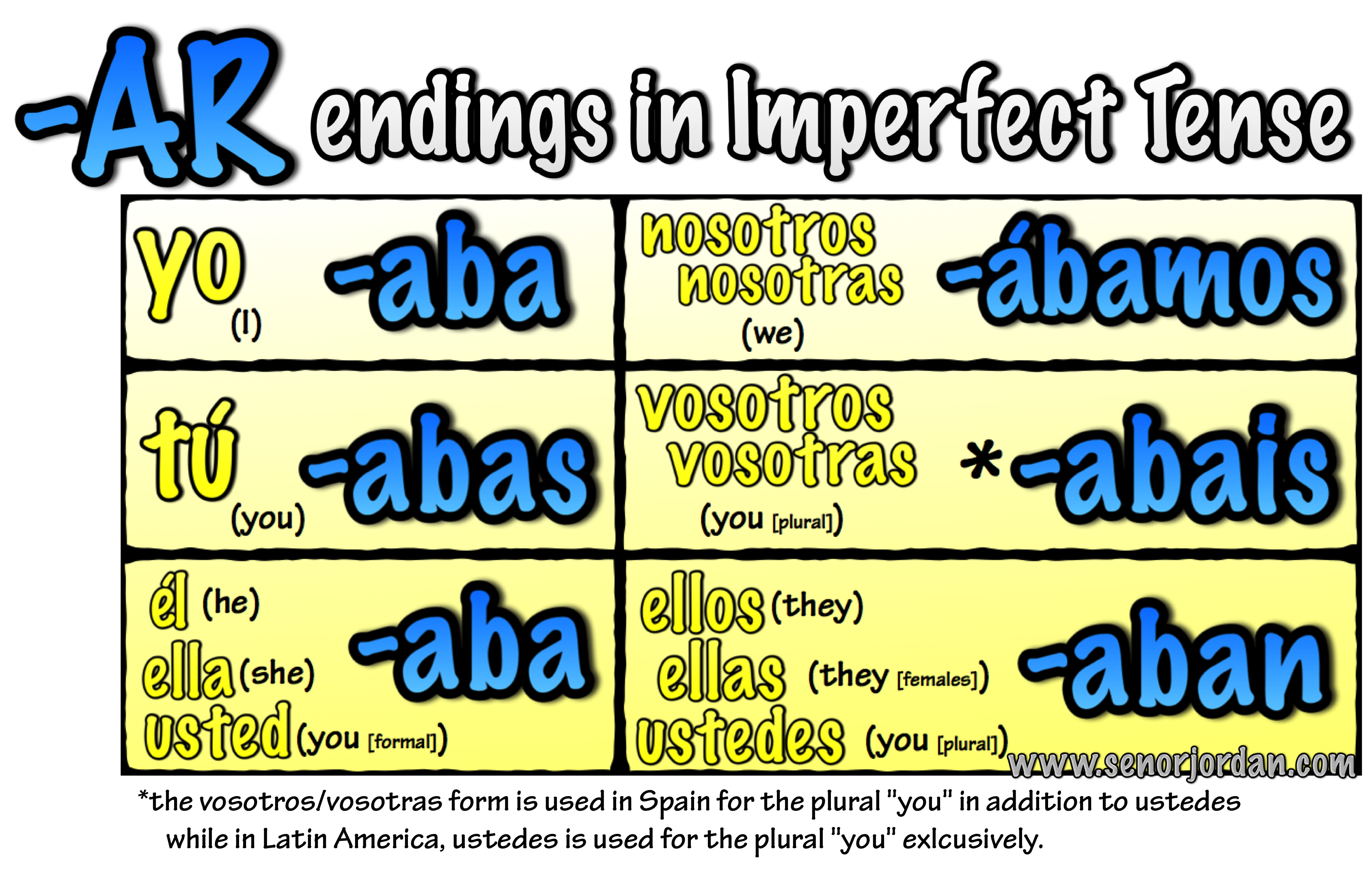
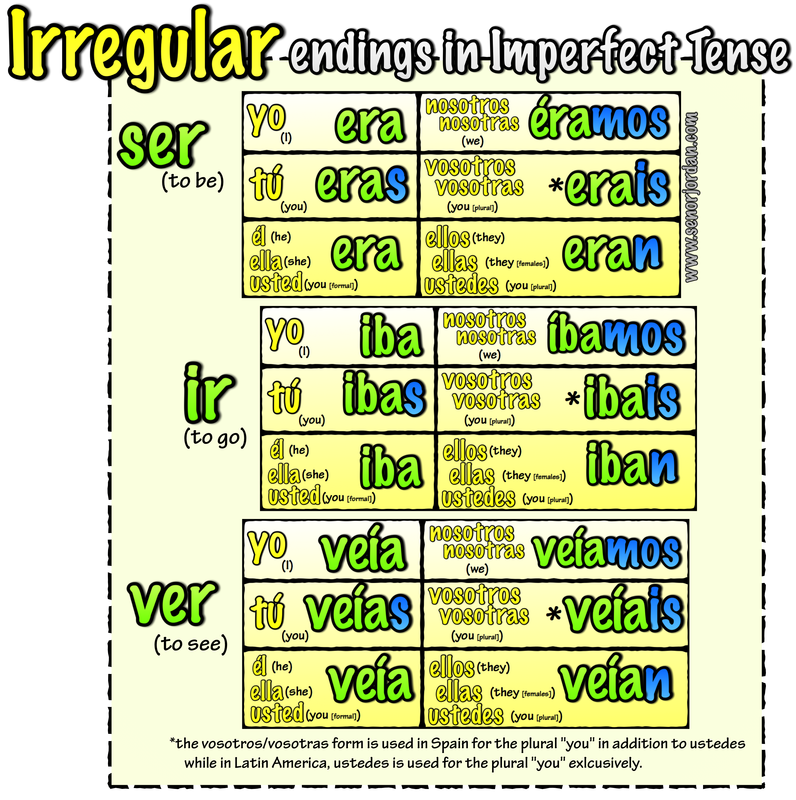
The preterite tense, on the other hand, is a past tense that is used to express a completed action. For example, the imperfect tense is a past tense that is used to express repeated actions or background information. Within each of these timelines, there may be more than one type in order to express a specific relationship to that time. So a verb in the past will look different than a verb in the present tense. This is for the past, the present, and the future. The tense refers to where in the timeline the action is happening. In Spanish, a verb’s ending will change based on the grammatical tense, the mood, and the subject pronoun. This way, by the time we finish, you’ll be able to express yourself using AR verbs, even in complex grammar tenses! Conjugating in SpanishĬonjugation is a process where the stem of the verb (the habl in habl ar ) remains the same, and the final part is changed to the appropriate ending.
Preterite endings spanish ar how to#
We’ll be going over how to conjugate all of these Spanish verbs in all of their forms. Today we are only going to be focusing on AR verbs. In other words, all verbs in Spanish are defined by the last two letters of their infinitive form. You have AR verbs, ER verbs, and IR verbs. Each verb is known by its infinitive ending. In general, there are three types of verbs in Spanish. Let’s get started! Types of Verbs in Spanish After this article, you’ll know the ins and outs of every kind of AR verb and you’ll be able to master ⅓ of all the verbs in Spanish.
So today we’re going to take the time to go over every single conjugation for AR verbs. It takes a bit of time because there are many irregular verbs to stack on top of the already-high number of regular verb conjugations. Since verb conjugation is such an integral part of the language, it’s a topic that is going to take some serious time and dedication to memorizing. The preterite is used for past actions that are seen as completed.When you first start studying Spanish, one of the first things you need to know how to do is how to conjugate Spanish verbs.

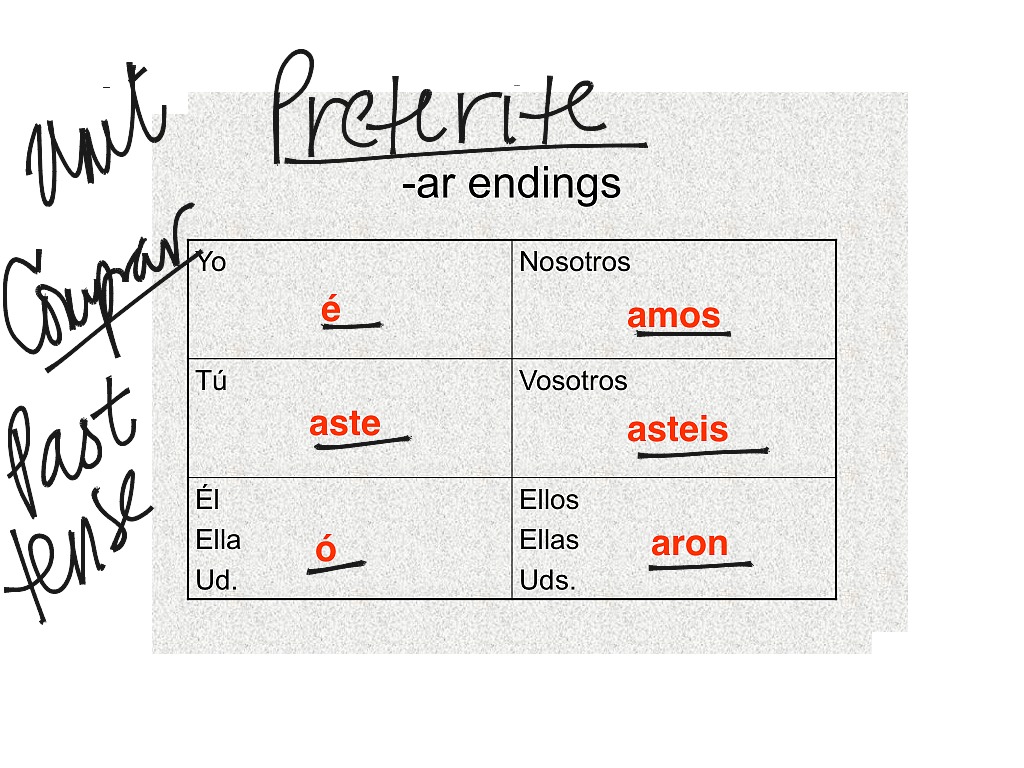
The above examples all fall within our general rule for using the preterite: It began to snow at eight in the morning. The preterite is used to state the beginning or the end of an action. The preterite is used for actions that were part of a chain of events.Įlla se levantó, se vistió, y salió de la casa. The preterite is used for actions that were repeated a specific number of times, or occurred during a specific period of time. The preterite is used for actions that can be viewed as single events.
Note: the nosotros forms for -ar and -ir verbs are the same in both preterite and present tenses: hablamos, vivimos. Here are all three regular preterite verb forms together: hablar To conjugate regular -er and -ir verbs in the preterite, simply drop the ending (-er or -ir) and add one of the following: To conjugate regular -ar verbs in the preterite, simply drop the ending (-ar) and add one of the following: In this lesson, you will learn how to conjugate -er and -ir verbs, and become more familiar with the uses of the preterite. You also learned how to conjugate regular -ar verbs. In the last lesson, you learned that the preterite is used for past actions that are seen as completed. Subjunctive VIII: Actions not yet completed Subjunctive III: Verbs that change orthographically Subjunctive II: Conjugating regular and stem-changing verbs


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
